Shop Now
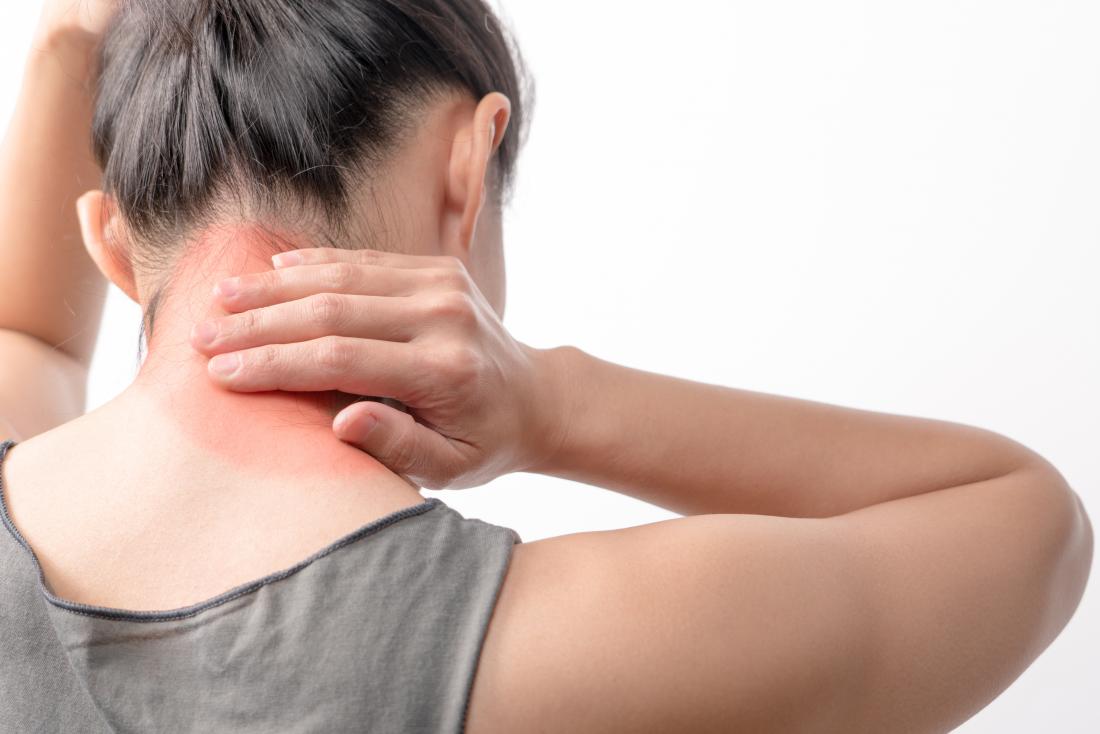
What is fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a disease characterized by widespread muscle pain. It can be defined as a form of soft tissue or non-articular rheumatism.

While experiencing pain, fibromyalgia patients also have to manage the following discomforts:
- Fatigue
- Burning sensation
- Stiffness
- Tension
- Muscle spasms
They also have to cope with side effects such as:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia and memory problems
- Mood changes
- Headaches and migraines
This condition primarily affects adult females and tends to gradually worsen over time or can be triggered by physical or psychological trauma or infections.
Causes of fibromyalgia
The exact causes of this condition are not clear (or at least not confirmed), but multiple factors are believed to play a role, including genetics, various infections, hormonal issues, and/or physical and/or psychological factors.
Symptoms of fibromyalgia
People with fibromyalgia frequently experience mild pain in muscles and joints, affecting different muscle regions, especially in sensitive areas known as tender points, such as the spine, neck, and shoulders.
The pain at tender points can be more intense, and a pain rating scale is used to estimate whether a patient has fibromyalgia.
Diagnosis is made after a person experiences persistent pain in symmetrical body parts for at least three months. If a patient scores at least 11 out of 18 points on a positive scale, they are likely to have fibromyalgia.
How to prevent fibromyalgia?

Unfortunately, these diseases cannot be prevented, but preventive interventions can be undertaken to slow down the progression of pain.
For example, hydrolyzed collagen can help regenerate collagen throughout the body and strengthen connective tissues (muscles, cartilage, and tendons) associated with the symptoms of this condition.
While it is not a curable disease, some supplemental treatments aimed at improving the daily living conditions of patients can be helpful.
Engaging in preventive measures helps avoid late-stage diagnoses, thus mitigating the intensity and acute symptoms of the disease.
